- with Inhouse Counsel
- with readers working within the Automotive industries
If a document is privileged before translation, it should still be privileged after without added risk, exposure, or loss of control.
Yet translation is often the weakest link in otherwise secure legal workflows, introducing hidden points of exposure that firms do not always see until something goes wrong.
This is why legal teams are increasingly turning to end-to-end encryption as a standard for protecting confidential data, personally identifiable information (PII), and legal privilege across every stage of the translation workflow.
Where Legal Translation Security Breaks Down
Every legal document passes through the same core stages during translation. When security is handled piecemeal, privilege can quietly break at any one of them.
What matters isn't whether security exists at a single point. It's whether protection holds from upload to delivery.
Because risk can be introduced at each stage, across both human and AI-assisted workflows, these stages provide a clear framework for identifying where security gaps most often emerge.
The 5 Stages of Legal Translation
Below are the five core stages every legal translation workflow passes through, highlighting where security commonly breaks down and how modern workflows address those risks.
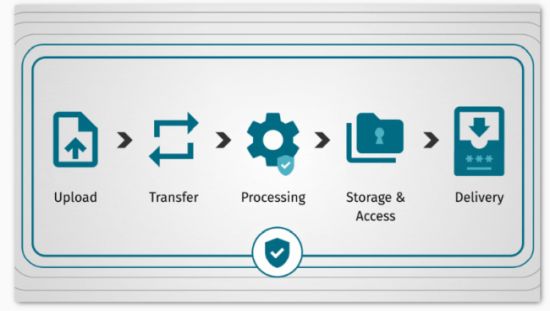
1. File Upload
Where security often breaks down:
Legal documents are commonly shared via email attachments,
unsecured portals, or open links before authentication, access
controls, or audit logging are applied. This exposes sensitive
information before translation even begins and puts legal privilege
and client confidentiality at risk from the outset.
What modern workflows do:
Files are uploaded through encrypted channels within a controlled
environment. Encryption ensures documents are unreadable to anyone
without authorization, even during transfer, eliminating unsecured
handoffs and preserving legal privilege from the first step.
2. Transfer
Where security often breaks down:
Legal documents are frequently transferred between multiple
vendors, platforms, or tools as part of the translation process.
Each handoff breaks visibility into who has access to the document
and when, creating gaps where content may be exposed or accessed
outside a firm's oversight and making it harder to defend
control over privileged material.
What modern workflows do:
Documents move through a controlled, encrypted workflow that
reduces handoffs between disconnected vendors or systems, helping
maintain consistent protection and legal oversight throughout the
process. By keeping transfers within controlled, secure
environments, legal teams retain control. Ensure your provider can
clearly identify all third parties involved in moving or handling
documents during transfer and maintain a complete audit trail of
who accessed files and when.
3. Processing
Where security often breaks down:
During processing, legal documents may be accessed by people or
systems that are not strictly authorized, whether through human
review, AI tools, or internal workflows. When access controls are
unclear or too broad, sensitive content can be viewed, copied, or
retained beyond what is necessary to complete the translation.
What modern workflows do:
Processing takes place within secure environments designed for
legal data, with controlled access and safeguards that help prevent
PII from being reused, retained unnecessarily, or exposed outside
the workflow. This ensures sensitive information and legal
privilege remain protected throughout translation, regardless of
whether processing involves human translators, AI, or both. Ask
your vendor if they limit processing access to authorized users and
systems only and prevent reuse or unnecessary retention of legal
content.
4. Storage & Access
Where security often breaks down:
Translated documents are frequently stored across shared drives,
local systems, or third-party platforms with broad or unclear
access permissions. When content is retained longer than necessary
or access is not tightly controlled, sensitive information can
remain exposed long after translation is complete, putting legal
privilege at risk.
What modern workflows do:
Documents are stored within secure environments with role-based
access controls and defined retention policies. Access is limited
to authorized users only, helping ensure sensitive information
remains protected and legal privilege is preserved throughout the
document lifecycle. Ensure your provider defines retention limits
and restricts ongoing access to translated documents based on role
and need.
5. Delivery
Where security often breaks down:
Final translations are often delivered via email attachments or
downloadable links that lack consistent security controls. Once
delivered, firms may lose visibility into who can access the
document or how it is stored and shared, increasing the risk of
unauthorized disclosure and weakening the ability to demonstrate
that privileged material remained protected after handoff.
What modern workflows do:
Translations are delivered through secure channels that maintain
encryption and access controls through final handoff. This ensures
protection holds through delivery and helps legal teams retain
control over sensitive documents until the very end.
Why End-to-End Encryption Is the New Standard
Legal translation is no longer a single task. It's a multi-stage workflow where documents move through systems, tools, and people, and security must hold at every point. As translation workflows evolve to include AI, automation, and multiple stakeholders, point-in-time protection is no longer enough.
End-to-end encryption ensures legal documents remain protected from upload to delivery, preserving confidentiality, PII, and legal privilege throughout the entire process. For legal teams evaluating translation solutions, the question is no longer whether security is included at one step, but whether it is built into the workflow as a whole.
Download the Legal A.I. Security Playbook to see what end-to-end protection looks like in practice and how to evaluate providers against this modern standard.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is end-to-end encryption in legal translation?
End-to-end encryption ensures legal documents remain encrypted and inaccessible to unauthorized parties from initial upload through final delivery, protecting confidentiality, PII, and legal privilege at every stage.
2. Why is translation a security risk for legal teams?
Translation workflows often involve multiple tools, vendors, and handoffs. Without consistent security controls, sensitive legal data can be exposed during upload, transfer, processing, storage, or delivery.
3. How does encryption protect legal privilege during translation?
Encryption prevents unauthorized access to legal documents while they are in motion or at rest, helping ensure that privileged information remains confidential throughout the translation process.
4. Can AI be used securely in legal translation workflows?
Yes. When AI is deployed within secure, controlled environments designed for legal data, it can support translation without compromising confidentiality or compliance requirements.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


