- within Insurance topic(s)
- in United States
- with readers working within the Insurance and Retail & Leisure industries
- within Insurance topic(s)
- in United States
- with readers working within the Banking & Credit industries
- within Insurance, Technology and Wealth Management topic(s)
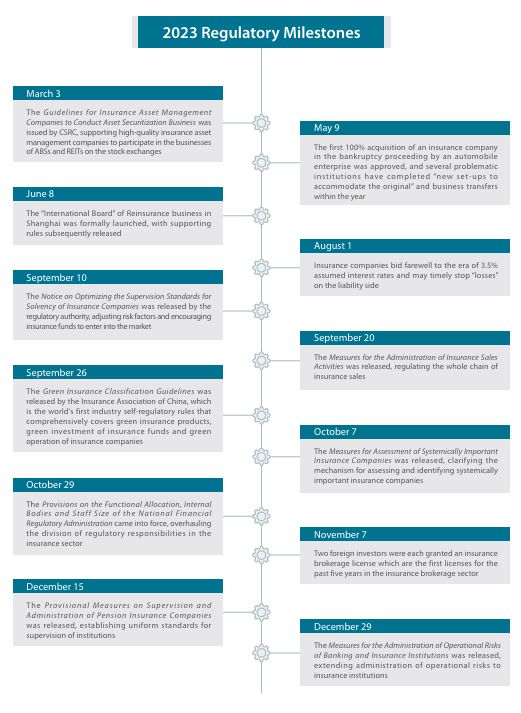
2023 Regulatory Mainline Review
01 Institutional reforms reshaping the regulatory landscape of the insurance sector
Since the merger of the former China Banking Regulatory Commission ("CBRC") and China Insurance Regulatory Commission ("CIRC") to form the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission ("former CBIRC") in 2018, the regulatory authority has gradually built and strengthened the institutional safeguards for the unified regulation of the banking and insurance sectors through these substantial institutional innovations. Five years later, the CPC Central Committee and the State Council issued the Reform Plan for Party and State Institutions in March 2023, reshaping the financial regulatory framework and the division of labor between central and local supervision. The National Financial Regulatory Administration ("NFRA") was established on the basis of the former CBIRC, and the day-to-day supervisory responsibilities of the People's Bank of China ("PBOC") for financial holding companies and other financial groups, as well as the responsibilities for financial consumer protection, and the investor protection responsibilities of the China Securities Regulatory Commission ("CSRC"), were transferred to the NFRA. The Provisions on the Functional Allocation, Internal Bodies and Staff Size of the NFRA (" 三定 " 方案 ) was released a few months later, in which the resetting of the functional departments and the division of responsibilities brought about a new normal for the supervision of the insurance sector.
With respect to market entry, a new Financial Institution Authorization Department has been established, transferring market entry and administrative licensing responsibilities previously dispersed among the various internal regulatory bodies to one special department. This may cause some short-term difficulties and challenges during any switchover period – since one special department may have information gap internally about any particular applicant's situation. However, in the long term, one special department can effectively align the form and substance requirements of different types of applications and improve the quality of approval work; at the same time, the unified regulatory standards can also effectively preposition the risk supervision gate and raise the threshold of market entry for the insurance industry.
With regard to regulatory bodies, the most notable changes are the merger of the former Department of Insurance Intermediary Supervision into the Department of Property and Casualty Insurance Supervision, and the merger of the former Department of Insurance Funds Utilization Supervision, the Department of Trust Supervision and the Department of Innovation to form the Asset and Wealth Management Institution Supervision Department. The former merge has aroused heated discussions in the market for a number of reasons. However, this adjustment certainly helped to confirm the positioning of insurance intermediaries as "channels", and creates convenience for regulatory activities and space for policy implementation from the perspective of "unity of reporting and behavior" and strengthening the regulation of sales practices. Amid such an atmosphere, the regulation of intermediates in the life insurance sector is expected to take shape soon. The Asset and Wealth Management Institution Supervision Department, establishment of which echoes the Guiding Opinions on Regulating Asset Management Business of Financial Institutions (the "New Asset Management Rules"), is dedicated to bring about unification of the regulatory standards applying to asset management products and thereby eliminate the space for regulatory arbitrage. As a corollary, it may have a more thorough penetrating review on the indirect investment of insurance funds through trusts, funds and other asset management products in supervising the use of insurance funds. Comparing with rules applicable to common asset management companies, those applicable to insurance asset management companies place an emphasis on the usage of insurance funds. In May 2022, the Standardization in the Insurance Industry during the 14th Five-Year Plan Period issued by the former CBIRC proposed to "promote the unification of standards for the asset management business of banks, securities, insurance and other industries". Once the unification of the higher-level laws and the regulatory organization structure has happened, it will be necessary to systematically analyze and align the rules covering the insurance sector.
02 Insurance sector serving economic and social development, devoted to the "five grand papers"
The Central Financial Work Conference held in November 2023 proposed that the financial sector should get devoted to the "five grand papers", promoting the high-quality development of science and technology finance, green finance, inclusive finance, pension finance and digital finance. In the past year, the insurance industry left a strong mark in the five areas around the theme of serving economic and social development.
With respect to science and technology finance and digital finance, the regulatory authority encourages leading insurance institutions to take the lead in researching and developing science and technology insurance products to underwrite various risks in the process of R&D and operation of enterprises; a lot of institutions also provide financial support for science and technology enterprises through private equity investment funds and equity investment plans, etc. In July, in response to the national governance upgrade on data security and cyber security, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and the NFRA jointly issued the Opinions on Promoting the Standardized and Healthy Development of Cybersecurity Insurance, which encourages insurance institutions to overcome technical difficulties and enrich cybersecurity insurance products and proposes opinions on measures to reduce insurance taxes and subsidize insurance purchases.
With regard to green finance, following the issuance of the Guidelines for Green Finance and related statistical systems by the former CBIRC in 2022, the Insurance Association of China (the "IAC") issued the Green Insurance Classification Guidelines and the Guidelines for Disclosure of Environmental, Social and Governance Information by Insurance Institutions in 2023, the former of which is also the world's first industry self-regulatory rule that comprehensively covers green insurance products, green investment of insurance funds and green operation of insurance companies. The above industry guidelines categorize many green scenarios with a very fine granularity, which facilitates the industry players to take the right place and start practicing.
With respect to inclusive finance and pension finance, a, various types of pilots in the previous period gradually entered into the stage of institutionalization and commercialization. The exclusive commercial pension insurance scheme launched as a pilot in 2021 became a regular business in 2023 successfully, with product terms and rates uniformly filed and administered, as with other personal insurance products. The scope of personal pension pilot products has been further expanded, and according to the China Banking Insurance Information Technology Management Company Limited (the "CBIITMC"), the number of personal pension insurance products on the market has greatly increased (there were just seven launched by six companies in 2022). The individual tax-deferred commercial pension insurance pilot products ceased to be sold from September 1, and the existing products were switched to personal pension products under the closed-loop management. At the same time, supervision of insurance companies follows the steps of supervision of the products. On December 15, the NFRA issued the Interim Measures for the Supervision and Administration of Pension Insurance Companies, emphasizing that pension insurance companies should focus on the main business of pensions (and not, for example, on short-term health insurance) and should not manage insurance funds or asset management products as a fiduciary. Following the opening of Guomin Pension Insurance Co. in 2022, there are now ten pension insurance companies in China. Compared with other types of life insurance companies, the regulatory requirements covering pension insurance companies are much stricter – covering everything from equity management, registered capital, corporate governance, and management of connected transactions to business concentration, which is also in line with the special function and important role of pension insurance companies to manage people's "pension money".
03 Tightening risk control on liability, unifying reporting and behavior
Investment yields on the asset side declined due to factors such as debt overdue storms and capital market shocks; however, channel costs are rising with fierce market competition, further weighing on the liability side and leaving some insurance companies with a more prominent risk of loss from difference of interest. In order to improve the asset quality of the liability side and resolve potential risks, the regulatory authority has repeatedly stepped on the brakes and introduced significant policy adjustments in 2023.
As required by the Ministry of Finance, eligible domestic and overseas listed insurance companies implemented the Accounting Standards for Business Enterprises No. 25 - Insurance Contracts as from January 1, 2023, which is aligned with IFRS17. The new standard adjusts the calculation method of premium income, requiring insurance companies to exclude the corresponding investment components and other non-insurance service components from premium income, whereby insurance companies are unable to adjust actuarial assumptions on an ad hoc basis to whitewash statements for the current period. The application of the new standard will have a direct impact on the performance of insurance companies, but it will also provide a truer picture of the company's operations and improve the quality of information on the liability side.
In January, NFRA fired the first shot in calling for the "unity of reporting and behavior" for the bank distribution channel of insurance companies, thereby uniformly setting the upper limit of the fee rate for bank distribution channel and reducing the cost of the liability side of the insurance institution. The Information fee, billing fee and other fees of various names, previously widely used to circumvent the regulation, are required to be strictly integrated into the management of channel costs, hence achieving the true " unity of reporting and behavior ".
In March, the regulatory authority released a significant signal to the market to lower the assumed interest rate, which caused a heated debate in the industry at once. The " assumed interest rate" is the interest rate used in pricing life insurance products, which has the characteristics similar to rigid redemption. In the context of reducing deposit interest rate and breaking the rigid redemption, this is a unique competitive advantage of insurance products in the market. However, high interest rates will increase the pressure on the liability side, and even cause loss from difference of interest. The regulatory authority has timely put on the brakes before the risk exposure and reduced the assumed interest rate from 3.5% to 3%.
In addition, the documents issued in 2023 for a variety of products repeatedly emphasized expense management and the implementation of the requirement of "unity of reporting and behavior" for the whole distribution chain of products. Administrative penalties were imposed on those found to falsify financial data, commit commission rebates, conduct false advertising, or make false claims, among other falsehoods and number of penalized institutions were larger and the levels of fines were higher than in previous years. In November, Li Yunze, Secretary of the Party Committee and Minister of the NFRA, said the next step would be to focus on strong and strict supervision--- equipping the supervision with "teeth and horn" in his words, .and to continue to enhance the supervision in terms of foresight, precision, effectiveness, and synergy. Controlling costs should help to guard against risks and promote the healthy development of the sector. We expect there will continue to be actions dedicated to "unity of reporting and behavior " in the next stage.
04 Investments in equity encouraged, and more real estate investment
In March 2020, the CSRC issued guidelines for stock exchanges to support insurance asset management companies ("AMCs") to start asset securitization and real estate investment trust fund businesses. Up to then, only qualified securities companies and mutual funds could invest in ABS and real estate investment trusts ("REITs"). The guidelines open up a new business area for insurance asset management companies, which can now participate in the ABS and REITs products of stock exchanges both as originators or managers. However, insurance asset management companies still need to obtain the approval from the industry regulatory authority to expand their business scope. In addition, one of the competitive advantages of insurance asset management companies is that they are backed by powerful insurance funds, so regulatory coordination and guidance are required as to how to carry out related product investment by insurance fund and the complicated regulatory guidance on related party transactions.
The NFRA and the CSRC have both sent strong signals that they want insurance fund to be invested in the market. In September, the NFRA issued the Circular on Optimizing the Solvency Regulatory Standards for Insurance Companies, which aimed to reduce the risk factors of investments in shares on the stock exchanges – such as CSI 300 Index constituent stocks, ordinary shares listed on the SSE STAR Market, and other equity investment instruments. The lower level of risk factors means that the relevant investment will occupy less capital, so as to guide insurance companies to make long-term layout in the capital market. According to the insurance business data released by the NFRA by December 2023, the investments by the insurance sector constituted some RMB27 trillion in total, of which investments in stocks and securities investment funds accounted for about 12.02%. This was a lower proportion than previously. The data explains the potential growth space on one hand, and on the other hand, tests how to further enhance the confidence of insurance enterprise investors in equity asset allocation.
Since the beginning of 2023, there has been a trend for insurance funds to invest in real estate, covering many types of properties such as commercial-office buildings, logistics parks, care homes and long term rental apartments. The redemption risks and the withdrawal of external funds of some real estate enterprises caused the valuation of many projects being returned to a rational level, and created an investment window for insurance fund. The regulations related to real estate investment have been in service for more than ten years, but in practice, the investment structure and the regulatory rules on financial products have changed with each passing day. After the reform of the upper management, there have been no major adjustments to the relevant systems and regulatory means in the short term, but we do not exclude the possibility of medium and long-term reviews and revisiting the relevant regulatory rules on the use of funds.
05 Significant risk disposal of many insurance companies, but work still needs to be done on small and medium-sized insurance companies
After five years of action involving risk disposals and restructuring by the middle of 2023, much of this work had been completed, the disposal of a number of institutions in risks has come to the end. In June 2023, the NFRA approved the opening of the business of Zhonghui Life and Ruizhong Life and in September approved the opening of the business of Higang Life. The newly established entities took over the insurance business and corresponding assets and liabilities of Tianan Life, Huaxia Life and Evergrande Life, respectively. In September, regulators gave their approval to establish Shenneng, which, it was generally assumed, would take over the assets of Tianan Insurance. Establishing new business to carry on the old ones has become a mature tool in the risk disposal of insurance industry, but each case requires a different approach, involving how much is invested in them and what their structures are. In certain cases, local state-owned enterprises and industrial organizations entered the market in different forms and insurance security funds participated therein in different degrees, which fully reflects the characteristic of adapting measures to the circumstances on a case-by-case basis in the risk disposal
The restructuring of E An P&C is the first time an insurance company in China has been restructured. The way it was done may serve as an example of how legislation is revised to deal with the bankruptcy of financial institutions. As revealed by the Beijing Financial Court, which sanctioned the bankruptcy, the China Insurance Security Fund acted for the first time as an agent after being legally authorized to declare claims on behalf of 7,641 policyholders. This provides a new approach to the disposal of insurance claims in follow-up projects. After the public recruitment of strategic investors in 2022, the wholly-owned acquisition of E An P&C by BYD was approved in May 2023. E An P&C's risk rating was subsequently upgraded from D to B which meets the standard.
In the latest comprehensive risk rating results of insurance companies (the second quarter of 2023) issued by the NFRA, 15 institutions were rated C (medium risk) and 12 institutions were rated D (high risk). All of them failed to meet the solvency standards. From this, we can see that China's insurance sector, particularly the small and medium-sized insurance companies, has some way to develop before the sector can claim to be mature. These sized companies are less exposed to risk and should therefore be easier to change to bring them in line with the overall approach to risk management and easy rectification. NFRA pointed out during its 2024 work conference that it will spare no effort to promote the reform and risk mitigation of small and medium-sized financial institutions, grasping the timing and effectiveness, and carrying out the work in a planned and step-by-step manner. At the same time, it is necessary to improve the normalization mechanism for financial risk disposal, implement the responsibilities of institutions, shareholders, senior management, regulators, local authorities, and industry participants, and promote the formation of collaborative efforts. Although the Financial Stability Law has not yet been formally enacted, this does not affect the active exploration of the government, industry regulators, judicial authorities, and market participants in risk disposal and mitigation models in practice.
06 License transactions are active, and foreign investors maintain confidence in China
In 2023, there was a certain amount of change of ownership in the insurance sector. Equities of several institutions are transferred publicly, and the changes to equities of several institutions have been successfully approved. The equity shares in these projects vary in size, but the underlying reasons share some commonality. Some state-owned shareholders, due to the requirement of "returning to the main business", have transferred their shareholdings in insurance companies; there are also some local state-owned assets acting in the opposite way and taking advantage of the situation to become the "blood transfusion" for insurance institutions.
Foreign investors have continued to be active in the M&A market. Overseas insurance giants Generali, ERGO, Allianz, AXA, and Chubb all increased their holdings or made major moves of internal restructuring in 2023, all of which reflect their confidence in and long-term planning for the Chinese business. What is also refreshing is that the regulator approved the licenses of two new insurance brokerage companies (i.e. BMW (China) Insurance Brokerage Co., Ltd. and ERGO Fangsheng Insurance Brokerage Co., Ltd.) on the same day of November 7. These two approvals break the five-year slump in the insurance brokerage market where no new licenses have been issued, and the background of the foreign shareholders has sent a strong signal of high-quality opening-up.
Through the activation of the equity investment exchange market, the survival of the fittest can be achieved through the market oriented approach at the early stage, so that shareholders without the ability to continuously make capital contribution can exit in an orderly manner. The case of the acquisition of E An P&C by BYD not only has far-reaching significance for the risk disposal field of financial institutions, but also sends a positive signal. In addition to state-owned capital and foreign capital, there are still many opportunities for private capital to invest in the financial sector as long as the investors comply with shareholders' qualifications and comply with regulatory rules.
07 Shanghai Reinsurance Business International Board Launched to Enhance the Say on the Financial Infrastructure
Following the former CBIRC and the Shanghai Municipal Government jointly announced the goal of building Shanghai into an international reinsurance center in 2022, the former CBIRC Shanghai Branch and the Shanghai Municipal Financial Supervision and Administration jointly issued the Implementing Rules for Accelerating the Development of Shanghai International Reinsurance Center in June 2023. At the Shanghai International Reinsurance Conference held at the end of October, the supporting rules for the "Reinsurance International Board" were officially issued.
The Reinsurance International Board is operated and managed by the Shanghai Insurance Exchange, conducting international reinsurance ceded business, international reinsurance ceding business, and domestic reinsurance business. It acts as a central platform for market player access, information management and regulatory intervention, including digital registration, clearing and settlement. Based on blockchain technology, the platform achieves the encryption and tamper-proof of data of all parties. On this basis, all parties conduct price inquiry and quotation, contract signing and depository, financial settlement, cross-border settlement and other activities through the platform. The platform fully plays the role of financial infrastructure.
The first batch of business rules focus on international ceded reinsurance business, which refers to the reinsurance arrangement of risks ceded by overseas cedants to domestic insurance companies or reinsurance companies. The rules cover many aspects such as business registration, transaction processes, data statistics, fee arrangements, and specific operations for the platform to adapt the default risk characteristic coefficients of C-ROSS reinsurance counterparties. In addition to complying with the relevant rules, the parties accessing the platform also need to enter into a service agreement with the platform operators to clarify their rights and obligations.
At the Sixth China International Import Expo in November, the first international ceded reinsurance treaty of the Reinsurance International Board was signed, marking the official launch of the ceded business. Interestingly, the direct insurance policy corresponding to the reinsurance ceded treaty is a cross-border auto insurance under "equivalent priority" policy for the Hong Kong motor vehicles, which gives multi-level significance to the "first policy".
08 Redrawing the Boundaries of Insurance Sales Activities and Emphasizing Financial Consumer Protection
At the beginning of 2023, the regulators issued a "sky-high price" ticket to penalize illegal platform operations, one of the reasons for which was the illegal participation in the insurance intermediary business. Third-party platforms' illegal business is currently mainly concentrated in the sales process. The sales of insurance products shall be carried out by licensed insurance companies and insurance intermediaries in accordance with rules. In September 2020, the Measures for the Administration of Insurance Sales Activities was issued. Although the new measures will only be implemented on March 1, 2024, market discussion has been very heated since the publication of the exposure draft in 2022. The new Measures not only fill the gap of the provisions on insurance sales, but also expand the connotation and denotation of insurance sales activities, listing the sales activities at the "front, middle and back" stages, and proposing the requirements on license-holding for the whole insurance chain. The sales activities are the same as the sales activities in the general sense, including communication, negotiation, offer and acceptance for the purpose of entering into a contract. However, the pre-sales and post-sales activities literally overlap with the businesses routinely engaged in by third-party platforms. For example, the acts of soliciting contract counterparties are similar to the "drainage" business. Next are the obligations such as delivery of policies, return visits, information notification, etc. In the process of cooperation between insurance companies and third-party platforms, these steps are often completed through the platforms.
Since the applicable provisions on internet insurance were amended, how to clarify the behavior boundary of third-party platforms has been an important subject for the study of market players. In 2022, multiple ministries and commissions will jointly issue the rules for online sales of financial products for consultation, showing a cross-industry unified trend. However, the Measures have not yet been officially issued, and the separate provisions on the sales of insurance products will undoubtedly bring new perspectives and challenges to the market in this period. NFRA has added new outsourced functions of the regulatory authorities and information technology service intermediaries to the "Three Fixed Plan", and relevant regulation may be further strengthened in the future.
Closely linked to the regulation of sales activities is the consumer protection of financial products. In 2023, the regulatory authorities issued documents on short-term health insurance, life insurance with a term of more than one year, group life insurance, term life insurance and whole life insurance, and vehicle insurance, among others. The documents require from a number of perspectives efforts on product disclosure, prohibit the "Magic Cube business", prohibit the use of misleading words such as "premium as low as (the minimum)" and "protection as high as (the highest)", and promote the standardization, popularization and simplification of the terms and conditions of products. In 2018, the APP of the BOC JinShiTong has opened an inquiry function called "sleeping insurance policy", which allows users to log in the platform to inquire about all the life insurance policies under their names in a one-stop manner. In the new round of institutional reform, the function of financial consumer protection will be closer to the NFRA. In the future, more unified provisions on financial consumer protection may be introduced.
2024 Regulatory Outlook
01 The Company Law Being Amended, Insurance Institution May Have More Choices in Governance Structure
At the end of 2023, the Seventh Session of the Fourteenth National People's Congress Standing Committee deliberated and passed the newly revised Company Law of the People's Republic of China (the "new Company Law"), which will be implemented from July 1, 2024. The revision of the new Company Law underwent three readings and numerous discussions. Among them, the adjustment to companies' capital requirements, which garnered the most discussion, has limited impact on insurance institutions implementing the paid-in capital system themselves. However, the new Company Law brings about new changes in various dimensions such as corporate governance.
Building upon the dual-tier governance structure of the original board of directors and supervisory board, the new Company Law provides market entities with more choices. "Qualified entities" may choose to establish only a board of directors without a supervisory board or supervisors. The supervisory functions can then be fulfilled by an audit committee established under the board of directors. However, within the current governance regulations covering the insurance sector, the supervisory board/supervisors are considered an indispensable component of the governance structure. Regulatory authorities may issue further guidance in the future to determine whether to provide insurance institutions with greater flexibility in choosing governance structures.
Furthermore, the new Company Law proposes a requirement for companies with more than 300 employees and no supervisory board or employee supervisors to have employee representatives on the board of directors. The concept of "employee directors" is not unfamiliar to insurance institutions, as there are provisions in the "Corporate Governance Guidelines for Banking and Insurance Institutions" encouraging the appointment of employee directors. However, in practice (especially for institutions in the form of limited liability companies), there are few cases of actually appointing employee directors. Insurance companies with a certain scale of branch network typically have a large employee base. In the process of implementing the requirements of the new Company Law, employee directors will undoubtedly have a more direct impact on company decisions at the board level compared to employee supervisors. How institutions will choose and how regulators will guide them is undoubtedly a topic of interest to the insurance market before the new Company Law officially takes effect.
In addition, the new Company Law has made modifications in the division of powers between different governance bodies and adjustments to procedural rules, which carry greater legal weight than the "Corporate Governance Guidelines for Banking and Insurance Institutions" and the "Guidelines for Insurance Company Articles of Association," documents currently widely relied upon when designing governance structures for institutions in the insurance sector. In order to comply with the requirements of the new Company Law, there may be widespread revisions to governance documents in the near future, and it is worth watching out for whether specific rules for regulatory coordination will be introduced at the industry regulatory level.
02 Stocks and Bonds Issuance Together, Strong Demand for "Blood Infusion" in the Insurance Company
Since the completion of the "Phase II" of the "C-ROSS" project more than two years ago, the rules of the second phase aimed to eliminate the excess capital in the system, bringing greater pressure and challenges to insurance companies. Supervisory authorities have provided transitional policies based on the principle of "differentiated supervision for different insurance companies" and plan to fully implement the new requirements no later than 2025. Over the past year, through quarterly data comparisons, the impact of the declining solvency adequacy ratio of some insurance companies continues, while the fiercely competitive market environment also demands a higher level of capital supply capability from insurance companies.
To improve solvency, a large number of insurance companies increased their capital in 2023, with most being continuous "blood infusion" from existing shareholders, aligning with the regulatory emphasis on reinforcing shareholder responsibilities in recent years. However, there have been cases where shareholders are unable or unwilling to participate in capital increases. Regulatory requirements mandate insurance institutions to include shareholders' obligations to replenish capital in their articles of association and further solidify shareholders' responsibilities through measures such as issuing notices on the "Regulations on Supervision of Major Shareholders' Behavior in Banking and Insurance Institutions (Trial)" and requiring written commitments from major shareholders. According to regulations, when regulatory authorities order insurance institutions to replenish capital, major shareholders who lack the capacity for capital supplementation or do not participate in capital increases may not obstruct other shareholders or investors from adopting reasonable capital increase plans. This system ensures the institution's right and possibility to seek fresh capital, but finding new capital for timely infusion remains a challenge for many small and medium-sized institutions.
In recent years, issuing capital replenishment bonds and perpetual bonds in the interbank market has become a new choice for insurance companies. Compared to equity injections, debt investments do not have strict shareholder qualification thresholds, allowing insurance companies to maintain governance stability while replenishing capital. It is expected that bond issuance will become the preferred choice for more institutions in the future. However, it is also worth noting that, according to current rules, there are thresholds for insurance companies to issue these two types of bonds. The issuer's own solvency must meet certain standards, and affiliated parties may not subscribe to each other's bonds.
03 Strong Momentum in the Development of Catastrophe Insurance and Agricultural Insurance Calls for Regulatory and Industry Institutional Construction
From personal health, life, and property safety, to corporate property and liability risk prevention, and further to the risk management of overall social governance, insurance services permeate every crucial aspect of economic and social development. The Central Financial Work Conference held in November explicitly called for the insurance sector to play its key role as an economic and society stabilizer. In line with the "top-level design" and overall regulatory approach, insurance sectors such as catastrophe insurance and agricultural insurance are showing strong momentum for development.
Following significant disasters, governments often bear the primary responsibility for rescue and post-disaster reconstruction. Institutions, on the other hand, utilize big data, remote sensing technology, and other means to develop catastrophe insurance and reinsurance products that meet market demands. This effectively enhances pre-disaster prevention levels and provides timely protection for life and property losses resulting from disasters. However, the construction of a catastrophe risk protection system requires joint efforts from market entities and the government, with the establishment of risk-sharing mechanisms and clear risk-bearing priority being imperative. At the institutional level, research on industry funds, catastrophe risk bonds, etc., will continue to advance, while at the market level, there may be more specific guidelines for micro-level product development and service standards.
In September, the State Council issued the Implementation Opinions on Promoting the High-Quality Development of Inclusive Finance, emphasizing the role of insurance, focusing on the development of agricultural insurance, and supporting agricultural production. Within the year, the China Insurance Association successively released the Guidelines for Agricultural Insurance Product Development and the Standard for Electronic Underwriting and Claims Handling of Agricultural Insurance. The former CBIRC issued the Regulations on Agricultural Insurance Actuarial Practices (Trial) in April, and later expanded the scope of implementation of full-cost insurance and crop income insurance for rice, wheat, and corn, from 13 major grain-producing provinces to all major grain-producing counties nationwide. Regulatory authorities further emphasized that the comprehensive premium rate for agricultural insurance should not exceed 20%, guiding more fiscal subsidies to be used for risk compensation. The future focus remains on the institutional design and policy support for agricultural insurance, and with the popularization of the market, there is an urgent need for further institutional safeguards for the "insurance + futures" financial product combination model.
04 Continuous Enhancement of Categorized Regulatory Mode Improves Management Quality and Efficiency
As early as 2009, regulatory authorities proposed the concept of "categorized regulatory supervision" for insurance companies. This approach evaluates and categorizes the risk levels of market entities from multiple perspectives, such as solvency, corporate governance, internal control compliance, fund utilization, and business operations, with corresponding differentiated regulatory measures. While categorized supervision may appear to increase the workload of regulatory information collection and reporting obligations for market entities, it effectively concentrates regulatory resources, provides more room for well-performing entities, and adopts more targeted measures for high-risk entities. This enhances the foresight, precision, effectiveness, and coordination of supervision.
Historically, at the end of 2008, regulations on categorized supervision of insurance professional intermediary institutions were introduced. After many years, regulatory authorities successively introduced categorized management systems in specific areas such as solvency and corporate governance. In 2021, they launched a regulatory rating method for insurance asset management companies. In 2023, draft opinions were issued for consultation on the categorized supervision methods for life insurance companies and the grading criteria for individual insurance agents. With the implementation of institutional reform plans, the model of categorized supervision and graded authorization may be implemented on a larger scale in the future. Among the existing categorized grading systems, there are overlaps in data requirements and reporting obligations. Whether or not there will be some degree of convergence in the future remains to be further sorted out and demonstrated.
05 Huge Demand for Cross-Border Insurance, Seeking the Right Timing for Institutional Construction
According to the Insurance Authority of Hong Kong, mainland visitors to Hong Kong spent approximately HK$59 billion on new insurance premiums in 2023, which surged by 27 times compared to 2022, marking a new high in nearly seven years.
Since the concept of "Insurance Connect" was first proposed in 2018, several years have passed. During this period, pilot programs for "equivalence recognition" of cross-border motor insurance, regional critical illness insurance, cross-border medical insurance, and other products have been conducted within the Greater Bay Area. However, the broader implementation of "Insurance Connect" has not been substantially realized.
Under current laws and regulations, domestic legal entities and other organizations that need to purchase insurance domestically are required to insure with domestic insurance companies. Moreover, if foreign insurance institutions wish to conduct insurance business operations in the mainland, they need to establish a commercial presence within the Mainland. The implementation of "Insurance Connect" requires coordination at the policy and institutional levels to address the differences in various aspects such as civil liability, industry regulation, tax supervision, and foreign exchange regulation across different jurisdictions. Previous initiatives such as "Stock Connect," "Bond Connect," "Wealth Management Connect," and "Swap Connect" have all faced similar challenges, to varying degrees. With the accumulation of experience from these interconnected products, regulatory authorities and market participants may jointly explore a practical and feasible path in the future.
In the absence of the implementation of "Insurance Connect," the sale of cross-border insurance products, especially cross-border insurance products under wealth management, remains a focus area for regulatory supervision. There is a possibility of subsequent introduction of more explicit or stringent regulations, measures, or stronger regulatory measures
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.





